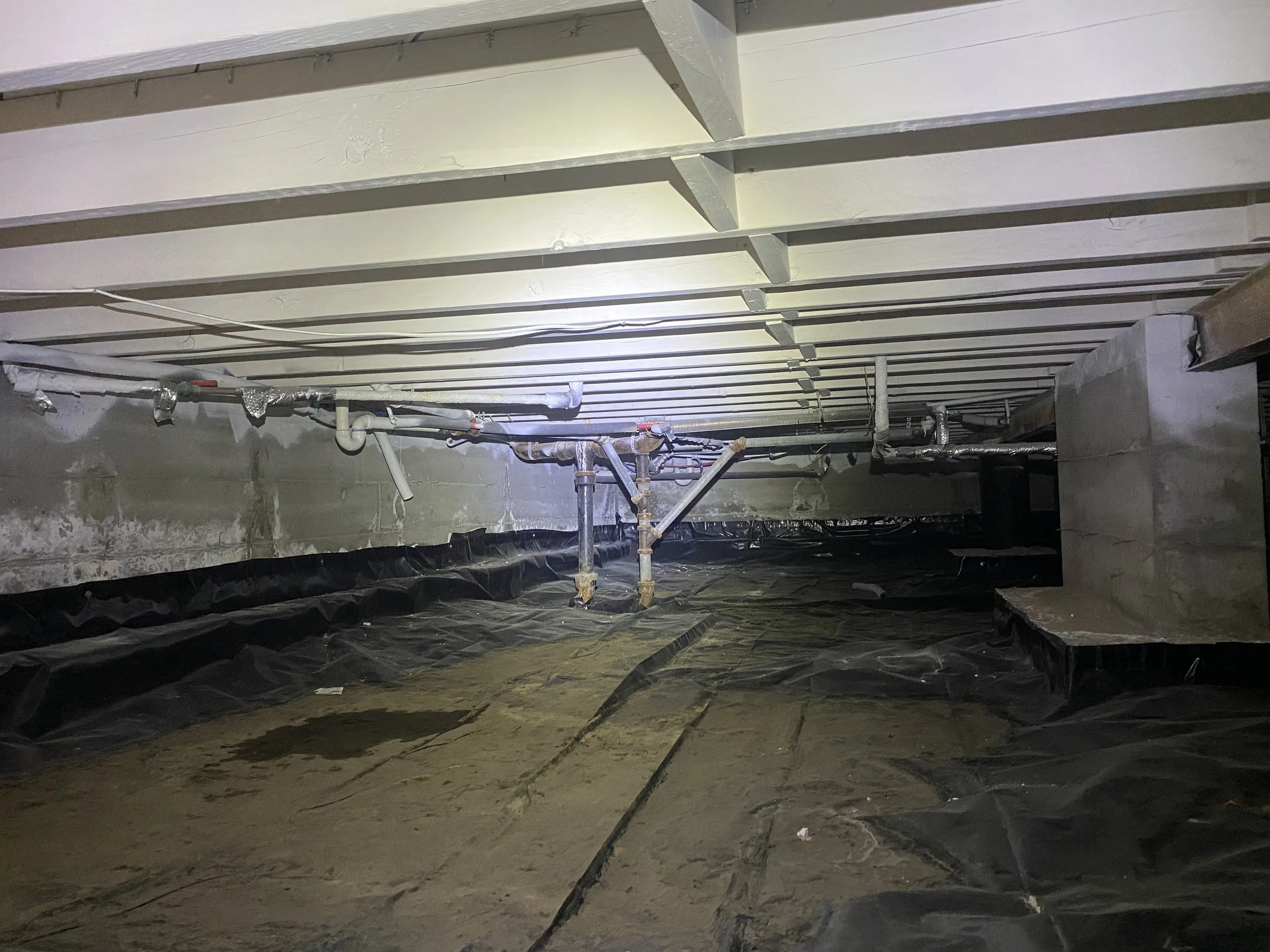
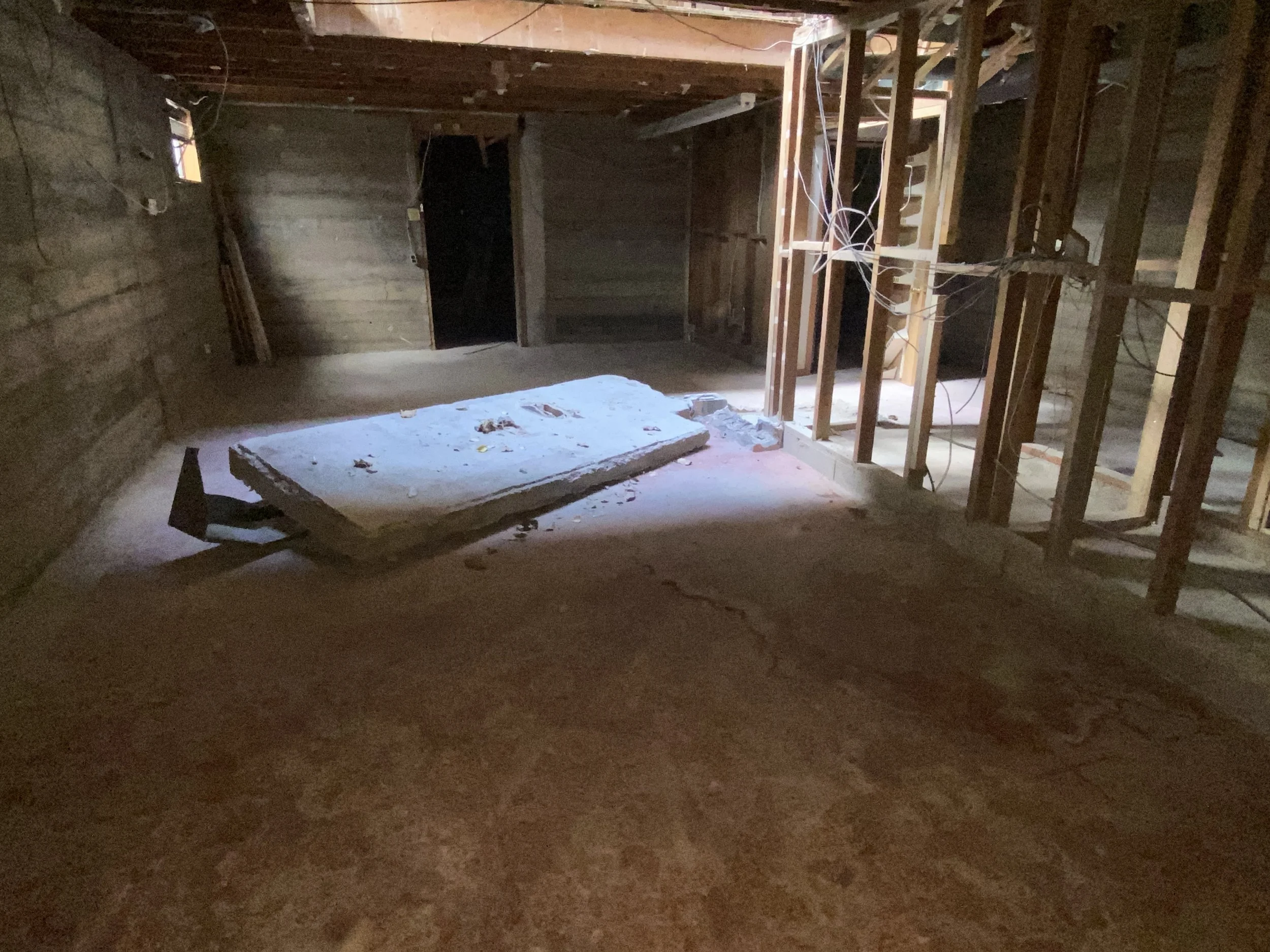
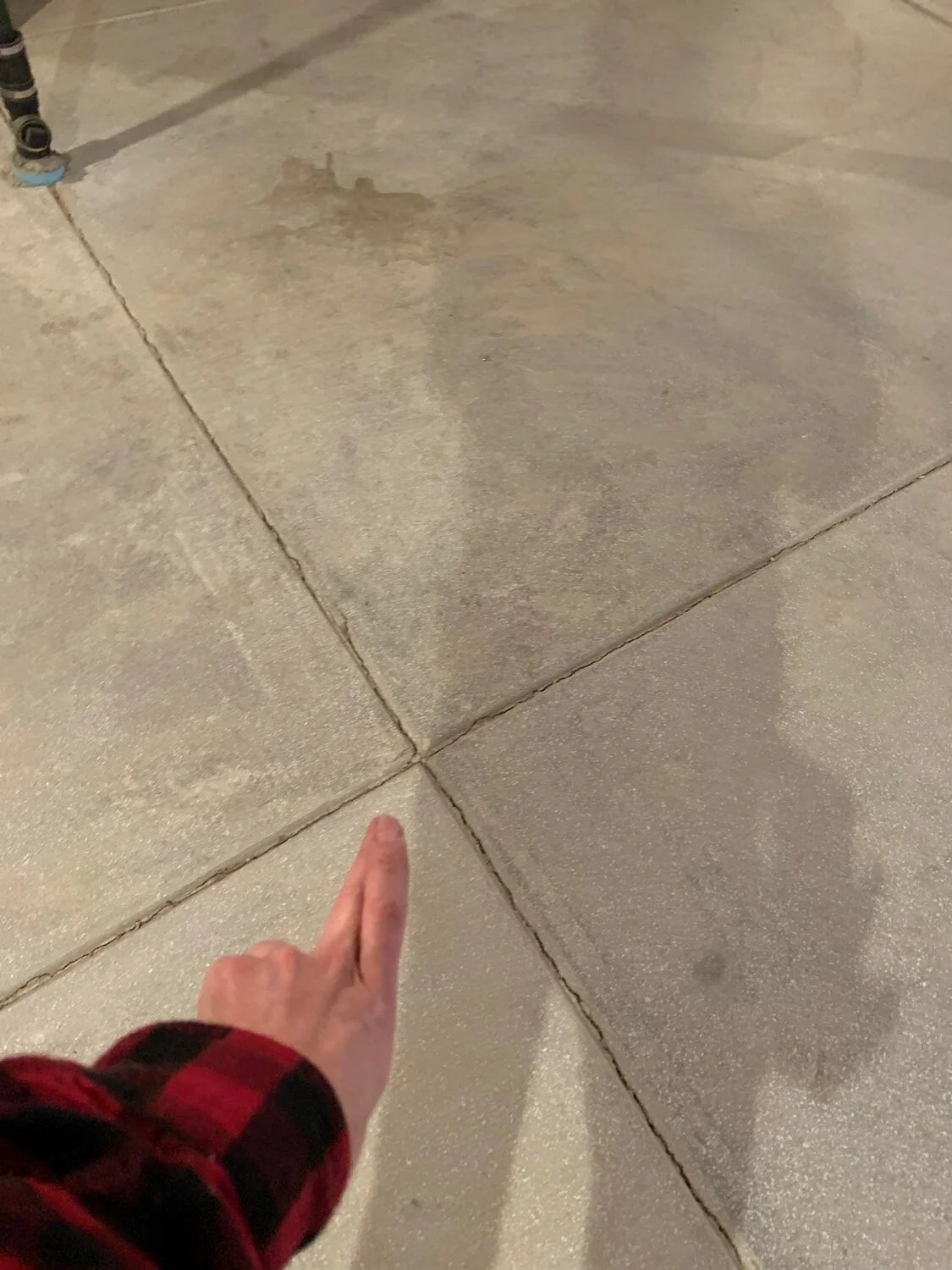
Crawl space foundations, while common, require proactive maintenance to prevent moisture intrusion, structural movement, and energy loss. Understanding how expansive soils interact with crawl space foundations can help homeowners protect their investment and ensure a stable, comfortable living environment.
What's Crackin'? Foundations and Expansive Soils in Colorado, Part 2: Basement Foundations
Basements are an extremely common feature in Colorado homes due to the region’s expansive soils and the need for additional living space. While basements provide valuable square footage and extra protection against the elements, they also introduce unique structural challenges. In this installment of our series, we’ll explore common basement foundation types, potential defects, and how to determine when foundation issues require further evaluation.
How Long Does A Deck Typically Last And How Often Should A Wood Deck Be Sealed?
The lifespan of a wood deck can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of wood used, the climate in the area, the level of maintenance it receives, and the amount of foot traffic and exposure to the elements it experiences.
In general, a well-built and well-maintained wood deck can last anywhere from 10 to 30 years or more.
To help extend the life of a wood deck, it's important to regularly clean it and inspect it for any signs of damage or wear, such as loose boards or rotting wood. Additionally, applying a high-quality sealant or stain to the deck can help protect it from moisture, UV rays, and other environmental factors that can contribute to deterioration.
The frequency with which a wood deck should be sealed can depend on a number of factors, including the type of sealant used, the climate in the area, and the amount of use and exposure to the elements the deck experiences.
As a general rule, however, most experts recommend that homeowners plan to seal their wood decks every 1 to 3 years.
Some signs that it may be time to reseal the deck include faded or discolored wood, rough or splintered surfaces, or water that no longer beads up on the surface of the wood.
Check out this rebate and tax credit calculator for Colorado Homeowners
Did you know that there are significant rebates and tax incentives available for Colorado homeowners to help offset the cost of home energy efficiency and electrification upgrades?
Sharing this info is a great touch point to your sphere, AND a potential way to leverage these rebates and incentives to help offset the repair or replacement costs of home inspection related repairs.
To help distill this information, we have put together our own local incentive resource guide here. You can also check out this helpful calculator from Rewiring America here.
Make sure to take advantage of these incentives whenever possible and to educate your clients about what’s available to them. We have also linked our resource guide to our home inspection reports for all relevant recommendations for ease of reference. The last thing we want is for someone to leave this money on the table.
As always, reach out to us with any questions.
What is the probability of Lead Based Paint pre-1978?
We all know that lead based paint (LBP) is a concern for pre-1978 homes, but did you know that the probability of LBP being present in a home heavily depends on its year of construction.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA):
Homes built before 1940, Appx. 87% contain lead-based paint.
Homes built between 1940-60, appx. 69% contain lead-based paint.
Homes built between 1960-78, appx. 24% contain lead-based paint.
The use of lead-based paint was banned in residential properties in the U.S. in 1978, so homes built after that year are unlikely to contain it. As with any environmental testing, the only way to confirm the presence of something is to test, but these figures can help you to better understand LBP risks by construction date.
Fortunately we now know that lead is a neurotoxin and should never have been used in household paint, but why was it ever used to begin with?
Durability - Lead in paint increased durability, longevity and moisture resistance.
Fast drying times - Lead sped up the paint drying process.
Color enhancement - Lead pigments provided brighter and longer lasting color.
Corrosion resistance - Lead helps protect metal from rust.
Lead is still permitted in certain industrial applications such as road and parking markers and in exterior industrial applications such as steel bridges, but was banned in residential paint and coatings in 1978.
How Recent LA Wildfires May Impact Colorado Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance in Colorado's foothills has become increasingly challenging since the Marshall Fire in December 2021, which caused over $2B in damages. The recent wildfires in Los Angeles and rising natural disasters nationwide are straining the insurance industry, and Colorado homeowners will feel the impact sooner than you may think.
Insurers are reassessing wildfire risks, potentially leading to:
Premium Increases: Higher rates in wildfire-prone areas like Colorado. Local insurers are now saying that it’s not just the foothills that are being assessed as high wildfire risk.
Policy Cancellations: Many carriers are not renewing policies in high-risk areas, especially the foothills.
Stricter Coverage Requirements: Homeowners may need fire mitigation measures (e.g., defensible space, home hardening) to maintain coverage. On site inspections will be required in many cases to obtain and maintain coverage.
Reduced Coverage Options: Some insurers may limit wildfire claims or cap payouts. The Colorado FAIR Plan will provide basic coverage, but it may come with challenges.
Now is the time to educate yourself and clients on fire mitigation. More to come on "Home Hardening" and what you need to know to keep your homes protected.
Why Window Replacements Aren’t the Top Energy Efficiency Fix
The window industry is going to hate me for this, but this is a topic that I have studied in depth since I began my education and career in the home performance profession in 2007.
When it comes to improving home energy efficiency, it’s a common belief that replacing windows should be the first step. While upgrading old windows does help improve home comfort and efficiency, it’s almost always not the most impactful or cost-effective home performance solution.
Here’s why:
Heat Loss Priorities: The biggest sources of energy loss are typically poorly insulated attics, walls, and basements/floors—not windows. Just think about how much surface area your windows account for as compared to your walls, floors and ceilings.
Cost vs. Benefit: High-performance windows are expensive, but their energy savings may take decades to offset the upfront cost. The cost of wall, attic and flooring insulation is relatively low.
Air Sealing is Key: Drafts and leaks around doors, vents, and other openings contribute significantly to energy loss. Sealing these gaps can have an immediate impact.
For the most impactful results and high ROI, prioritize insulation and air sealing, then consider window upgrades as part of a long-term energy plan. Investing in these areas first ensures the greatest return on your energy efficiency improvements.
With that being said, every home is different and it’s always best to start with a comprehensive Home Energy Audit to assess, determine and prioritize your options for energy efficiency optimization. While we have deep roots in home energy audits, we do not currently offer this service, but do have some local recommendations on our Home Service Provider list.
Significant rebates, tax credits and incentives are available for home energy audits and home efficiency upgrades through the utility companies and on the local, state and federal level. Be sure to check out our Energy Efficiency and Electrification Resource Guide for more information.
Foundation Moisture Prevention
We have said it before, and we will say it again and again. Moisture management is critical when it comes to your home. We have seen firsthand how proactive steps can save homeowners from major headaches down the road, and conversely how improper moisture management has caused floods, structural issues and mold. Below are some tips to know and share.
Ensure Proper Grading Around the Home
The ground should slope away from the foundation at least 6 inches over the first 10 feet. This helps direct water away from the house.
At the very least, just make sure that water is draining AWAY from the home.
Maintain and Extend Downspouts
Downspouts should discharge water at least 4-6 feet away from the foundation.
Recommend installing downspout extensions to prevent water from collecting near the foundation.
Clean and Repair Gutters
Clogged or damaged gutters can cause water to overflow and seep into the foundation. Water spilling over from clogged gutters led to a lot of basement flooding last year during the heavy rainfalls that hit the Denver-Metro area.
Regularly clean gutters, especially in the fall.
Suggest ensuring all gutter joints are sealed and securely attached.
Install a French Drain or Drainage System
If the property has a history of water pooling near the foundation, recommend consulting a professional to install a French drain or other drainage solutions.
Check for Cracks in the Foundation
Small cracks can allow water to seep in. Inspect the foundation regularly and use an appropriate sealant to fill any minor cracks.
For larger cracks, suggest consulting a structural engineer or foundation specialist.
Maintain Proper Landscaping
Trees and shrubs should be planted at least 5-10 feet from the foundation to prevent root intrusion and soil moisture issues.
Opt for native plants that require less water, reducing the risk of over-saturating the soil.
Install a Sump Pump
In areas prone to heavy rainfall or high water tables, a sump pump can help remove excess water from around the foundation.
Recommend testing the sump pump regularly to ensure it's operational.
Waterproof the Basement or Crawl Space
Suggest using waterproof paint or sealants on basement walls to reduce moisture intrusion.
Install a vapor barrier in crawl spaces and ensure that it’s properly sealed.
Monitor Drainage After Heavy Rain
Walk around the property after a rainstorm to check how water is draining and identify any problem areas early.
Why are old Denver homes all made of solid brick?
The answer to this question dates back to April 19, 1863 when a fire broke out in a building between Blake and Market Street in what we know today as LoDo. The fire spread rapidly due to the predominance of wooden buildings and destroyed approximately 50 buildings, including stores, hotels, and other businesses along Blake, Market, and Larimer Streets.
After the fire, Denver's residents and city officials realized that the extensive use of wood in construction posed a major fire risk. As a result the Brick Ordinance was born. The ordinance led to a shift away from temporary wooden structures toward more durable and fire-resistant materials, helping prevent future large-scale fires and improving public safety. The ordinance led to a shift away from temporary wooden structures toward more durable and fire-resistant materials such as brick and stone.
Given Denver’s abundance of clay, brick construction was accessible and became the standard of commercial and residential construction for nearly a century to follow. For more information on this piece of local history, check out the below article from Colorado Public Radio.
How Much Does A Standard Garage Door Tuneup Cost And What Does It Include?
A garage door and opener servicing generally costs between $120-$150, but many companies will run door service specials periodically for less than $100.
Routine garage door and opener service typically includes a comprehensive inspection of panels, hinges, bearing, cables, drums, track and opener for any irregularities. This also typically includes re-tensioning the springs for proper balance as well as making any adjustments to the door to make things run as smoothly as possible. A garage door technician should also check the opener limits and sensitivity to ensure safe operation.
How often should a garage door be maintained and why is routine maintenance important?
Garage door professional, Louis Wilson, of Ascent Garage Doors recommends that garage doors should be serviced annually or at least every other year in order to maintain proper spring balance and make sure there isn’t any progressive failure of components that could cause larger problems.
Many people don’t realize it, but a garage door is the largest moving part of a home and can present safety issues if not properly serviced. Regular service greatly reduces the risk of large problems with your door coming off track, getting stuck, or even panels falling, which is a huge safety hazard.
HomeBinder - Utilizing Technology to Help our Clients Beyond the Home Inspection
What's Crackin'? Foundations and Expansive Soils in Colorado, Part 1: Slab-on-Grade
One of the most common observations we come across inspecting homes in Colorado are cracked foundations, most commonly made of poured concrete, concrete masonry units or brick. This issue is also a higher priority item a potential buyer may consider when deciding to go forward with or walk away from the purchase of a home.